Wifiphisher
is an open source framework that can be utilised for red team
engagements for wireless networks through Man in the Middle attacks. The
tool is capable of using the modern wifi association techniques, such
as Known Beacons, KARMA, and Evil Twin. With the ‘Known Beacons’
technique, Wifiphisher broadcasts ESSIDs that are known to the audience.
KARMA is a masquerading technique where Wifiphisher acts like a public
network. Evil Twin is the most common technique where rogue access
points are created. Moreover, the tool can also be used to launch
phishing attacks for stealing social account credentials and payload
injections against wifi clients.
Wifiphisher Installation
Wifiphisher requires a wireless network adapter that must be capable
of packet injection and support monitoring mode. Wifiphisher is
supported by Linux OS with Kali Linux as the officially supported
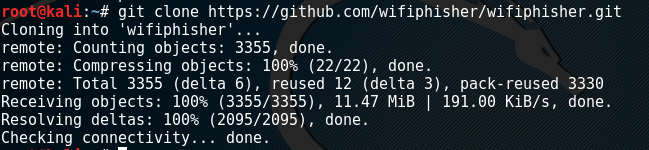
distribution. The installation can be performed by cloning the tool from
Github using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/wifiphisher/wifiphisher.git
After cloning the tool, move to the Wifiphiser directory and run the installation file using the following command.
cd wifiphisher
sudo python setup.py install
How Wifiphisher Works
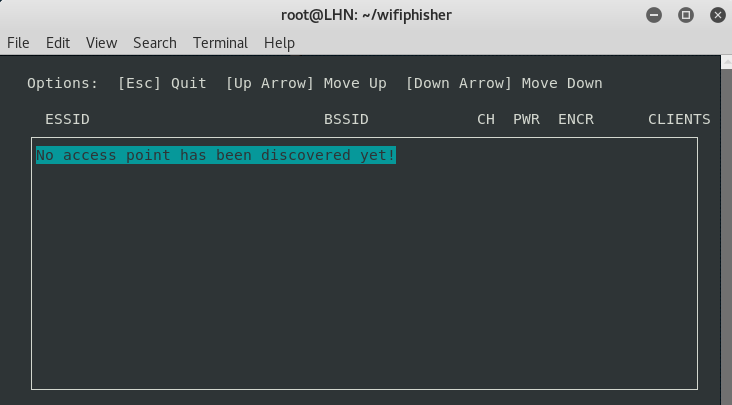
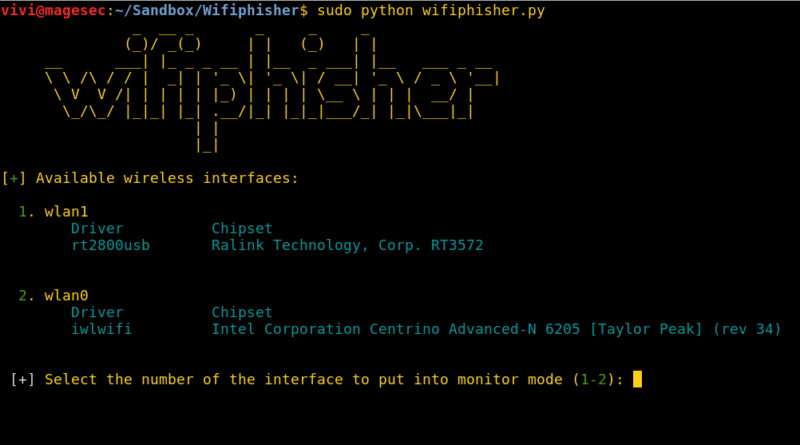
Wifiphisher can be launched with or without any parameters or options. To run the tool without setting any options, just type wifiphisher or python bin/wifiphisher
in the terminal. The tool looks for the appropriate wifi interface and
opens in a GUI mode as shown in the following screenshot.
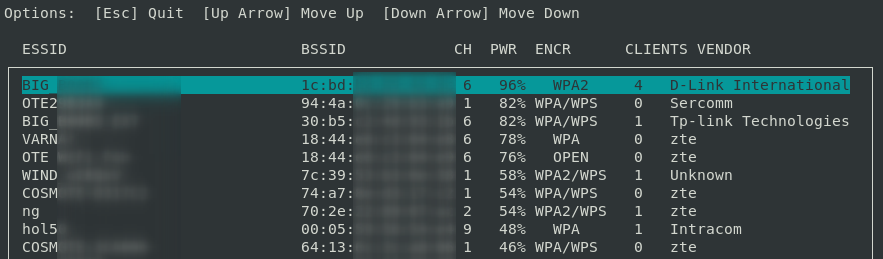
After the GUI interface is open, the tool searches for available wifi
networks (ESSIDs) in the surrounding area. The target ESSID can be
selected through the up/down arrow keys.
As mentioned earlier, the tool is capable of performing all the
modern MITM WiFi attacks. KARMA and Evil Twin are the default attack
modes of Wifiphisher. The Evil Twin attack can be performed by running
the tool with the following command options.
wifiphisher -aI wlan0 -jI wlan1 -p firmware-upgrade --handshake-capture handshake.pcap
The above command uses wlan0 interface as a rogue access point where
victims can connect. The wlan1 with –jI flag is used to launch a Denial
of Service (DoS) attack. The DoS attack prevents users from connecting
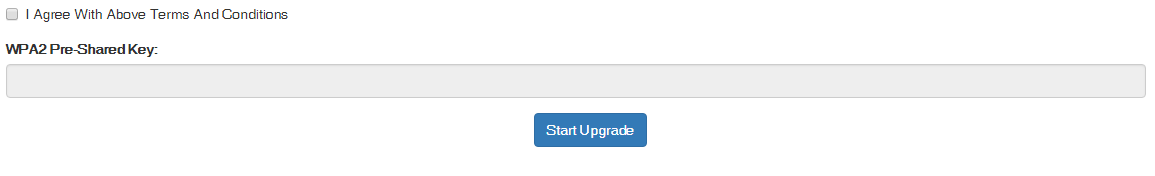
to the real access point. The firmware-upgrade option is displayed to
the users to enter the wifi key to connect and upgrade the (fake)
firmware. The handshake argument in the command verifies that the user
provided key is authentic.
Wifiphisher is not limited to stealing WiFi credentials. It can be
used to inject malicious code/malware into a victim’s machine using
plugin-update scenario.
wifiphisher --essid Office_Wifi -p plugin_update -pK <Pre-shared Key>
The above command sends a plugin update option to the ESSID named as
Office_Wifi. The WiFi key (pre-shared key) is known to the attacker in
this scenario. Victims who perform the plugin update task actually
download malicious code in their machines. The code can be a malware or a
shell that can provide remote access to the attacker. Similarly,
Wifiphisher can also be used to steal social network credentials of the
users.
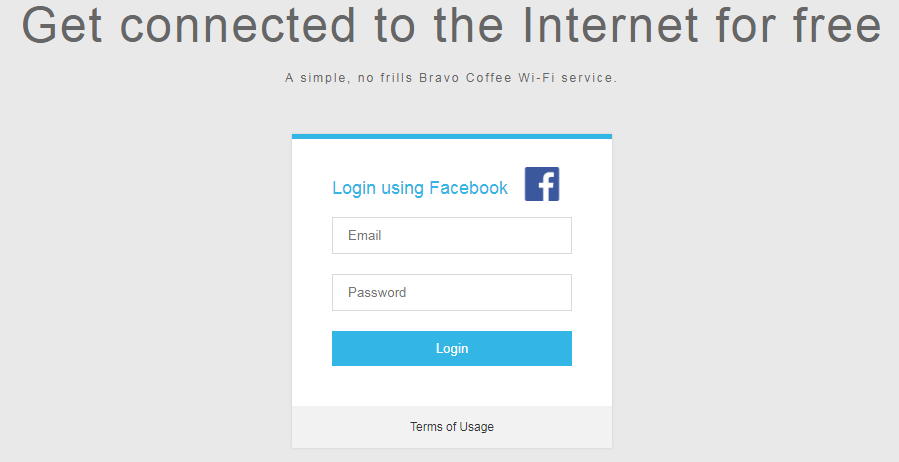
wifiphisher --noextensions --essid "Free wifi" -p oauth-login -kB
The above command asks the users to connect to the Free wifi ESSID by entering their social account credentials like FB.
![Author Image]()








Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire