The
Evil Access Point (AP) attack has been around for a long time. There
are several ways to create this attack and mitmAP is a python based tool
to make it simple for you. Combining the power of various tools, such
as SSLstrip2, Driftnet, tshark, wireshark, mitmproxy and more, you can
create a fake AP and sniff the data of whoever connects to it.
Installing mitmAP
Pretty straightforward installation just clone the Github repository to your Kali machine.
git clone https://github.com/xdavidhu/mitmAP.git
Then just run it with python3 and it will install all the missing dependencies automatically.
cd mitmAP/python3 mitmAP.py
Press ‘Y’ and you are good to go.
Running mitmAP
As before run again ‘python3 mitmAP.py‘ to get into the interface of mitmAP.
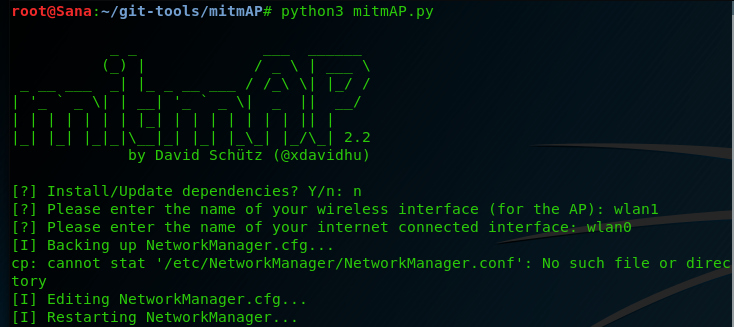
You will need 2 network interfaces – one to act as the AP device and
the second as the WAN connection. Simply put, one is used for the victim
to connect to and the second to have the victim connect to the
internet. I have my external USB card to act as the AP (wlan1) and my
built-in wireless card (wlan0) to act as the WAN connection. Use
‘ifconfig’ to see your internet interfaces and change them accordingly.
Next you will be asked if you want to use SSLstrip2, which is a tool
that helps you downgrade client connections from HTTPS to HTTP. Press
‘y’ and the second option is if you want to use Driftnet, which captures
unencrypted images of a client. Press also ‘y’. Then enter a name for
your AP, which channel you want it to perform (generally ‘1’ is good)
and then, if you want to add WPA2 encryption. This is optimal, if you
want to target a specific AP and want to mimic the same password. In our
example we just create an open AP, so we don’t have to add a password.

I don’t want to put a speed limitation to our client. Also, I’m good
with tshark, so I don’t have to use wireshark too. You can change these
options as you wish.

That’s it! Your AP is all set and fully functioning. All you have to
do now is wait for the user to connect to your evil AP. If a victim
connects to you, you will see the connection as shown below.

When you want to terminate the process just press ‘Ctrl + C‘ 2 times. The data that you sniffed will be stored in the ‘/mitmAP/logs‘
folder. If the victim typed any password you can type this command to
see if you got any luck(it’s not always the same command).
grep -a (name of the site) mitmap-sslstrip.log | grep passwd --color=always
![Author Image]()






Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire